KV value flow coefficient of the stop valve
The KV value (also known as the flow coefficient or CV value in some regions) of a valve is a measure of its flow capacity. Specifically, it represents the volume of water in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) that will pass through the valve with a pressure drop of 1 bar (100 KPA or approximately 14.5 psi) across the valve.
The formula for calculating the KV value is: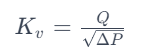
Where:
Kv is the valve flow coefficient in cubic meters per hour (m³/h).
Q is the flow rate of the fluid in cubic meters per hour.
ΔP is the pressure drop across the valve in pascals (Pa).
The higher the KV value, the greater the flow capacity of the valve. The KV value is crucial for selecting and sizing valves to ensure they can handle the required flow rates in a given system.
It's important to note that the KV value is typically determined experimentally for a specific valve under specific conditions. Engineers use this value to compare different valves and select the most suitable one for a particular application, ensuring that it can provide the desired flow performance under specified pressure conditions.
In some regions, such as the United States, the term "CV" is used instead of "KV," and the relationship between them is CV = 1.17 × KV. The choice of terminology often depends on regional or industry standards.
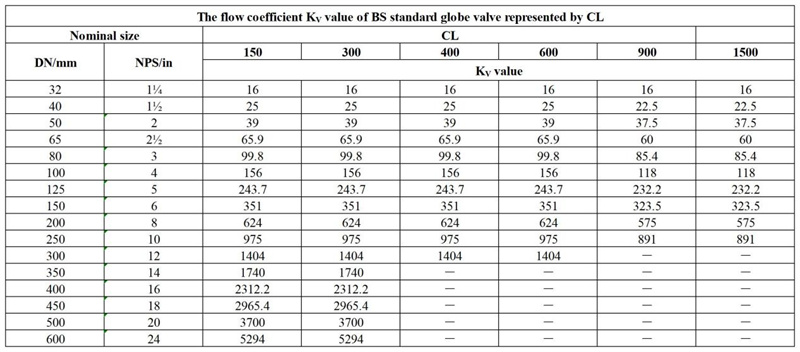
Here, we will share the flow coefficient KV value of BS standard globe valve represented by CL.

 Tel: +86-577-67926789 / +86-577-67927781
Tel: +86-577-67926789 / +86-577-67927781 E-mail:
E-mail: 








